IRT Robot Systems
Since 2006, Tokyo University has been supporting the "Information and Robot Technology Research Initiative". Through this project, we create platforms to forward IRT innovation and imagine scenarios where these platforms can support Japan's aging society and its people. These platforms include humanoid robots, daily life assistance systems, and personal mobility systems. We aim to create robotic devices, IRT management systems, IRT environments, and cyber interfaces that can be put into practical use for Japan's aging society. At JSK, the IRT Robot System Research and Development Group is in charge of this project.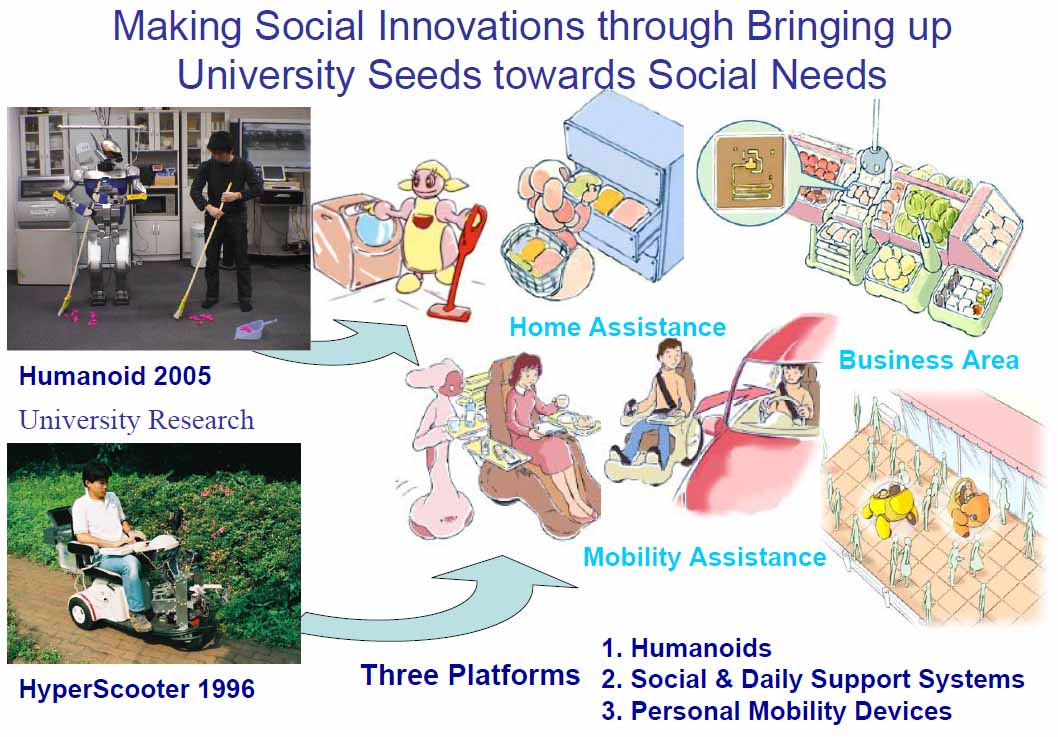
Research Objective
We are aiming to create safe, human- and environment-friendly atonomous humanoid robots and personal mobility systems that can perform situation recognition based on observation and learning and understand human intentions. We also aim for an automatic movement generation hardware-control program and high-level integrated software base for the implementation of a multi-agent system.
- Papers
- M. Inaba, K. Okada, T. Yoshikai, R. Hanai, K. Yamazaki, Y. Nakanish, H. Yaguchi, N. Hatao, J. Fujimoto, M. Kojima, S. Tokutsu, K. Yamamoto, Y. Kakiuchi, T. Maki, S. Nozawa, R. Ueda, I. Mizuuchi: Enhanced Mother Environment with Humanoid Specialization in IRT Robot Systems, in Cedric Pradalier and Roland Siegwart and Gerhard Hirzinger (Eds.): Robotics Research: The 14th International Symposium ISRR, pp.379--396, Springer, 2011.
- Kei Okada, Mitsuharu Kojima, Satoru Tokutsu, Yuto Mori, Toshiaki Maki, Masayuki Inaba: Integrating Recognition and Action Through Task-Relevant Knowledge for Daily Assistive Humanoids, Advanced Robotics, Vol.23, No.4, pp.459--480, 2009.
- Masayuki Inaba: Robot System Research in the Center of IRT, The University of Tokyo, in The 25th Annual Conference on Robotics Society of Japan, 1L36, 2007.
- Masayuki Inaba: Robot Systems Research in the IRT Innovation Project, in The 24th Annual Conference on Robotics Society of Japan, 2M13, 2006.
Humanoid
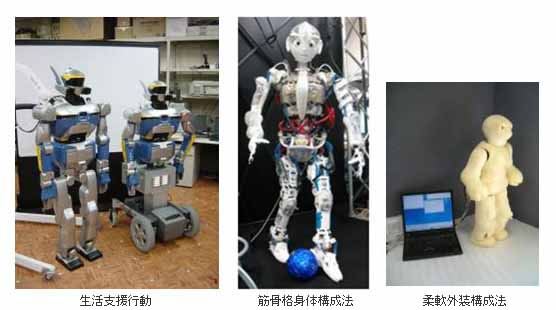
- A human-form robot platform that can understand human actions within a human-made environment, model human abilities, and support humans in daily tasks
- Skills include: walking, stabilization, audiovisual recognition, paired arm coordination, tool manipulation, full-body movement, reversion to standing position after a fall, full-body sensing, a muscle tendon-like driving system, and full-body dynamic movement
Personal Mobility

- A robot platform that expands the range of mobility for an individual, letting a human board it and seamlessly move within and outside of a room
- Skills include: high operability motion control, obstacle detection, automatic movement, human-interaction functionality, emergency braking for danger avoidance, environment recognition, view sequencing, position awareness
Technology for Recognition-Learing-Action Integration

Daily Assistive Robot (Left) Tool-manipulation (Right)
- Ability to integrate perception and behavior, ability to learn based on self-judgment of resulting behaviors and human interaction
- Skills include: real-time vision tracking, audiovisual processing, area memory data processing, gaze control, statistical pattern recognition, space planning, SLAM, memory usage processing, Bayesian networks, reinforcement learning, probability-based reasoning
Technology for Adaptation to Humans and the Environment

Intelligent Learning by Watching
- Has the ability to recognize its situation based on observation and learning, and the ability to understand human intention. It can adapt its behaviors to humans and the surrounding environment.
- Skills include: visual recognition and intention estimation based on human behaviors, imitation, human interaction, environment sound recognition, flexible limbs, haptically-based movement, integrated automatic component management, chronological data processing, probabilistic and statistical data processing
IRT Software Foundation
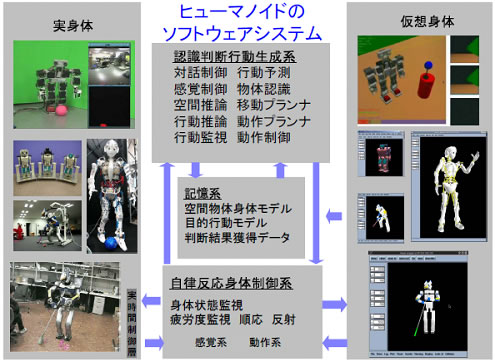
Integrated Software System for Real-Model Body

Mother Environment for Robot Body-Brain System
- With the ability to work over a large-scale network, this low-memory load yet high-efficiency data processing system ties together the robot and its interactions with the real world.
- Characteristics include: a parallel object-oriented programming languaged used for artificial intelligence applications, a built-in geometry modeling system, real-time memory management, network distribution programming, built-in real-time processing, an event processing system, online debugging, control program generation
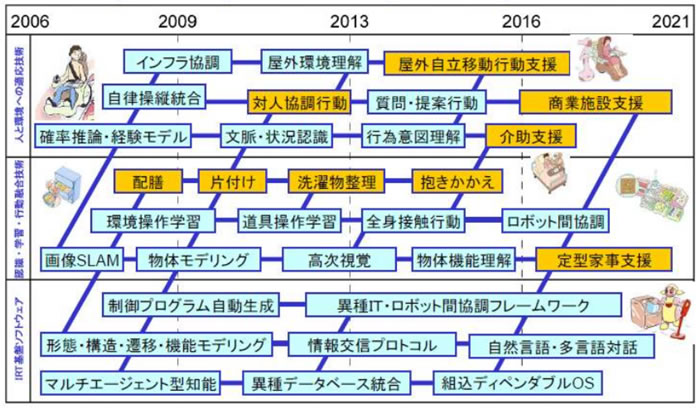
Roadmap